To begin with, Propecia (finasteride 1 mg) is a prescription medication approved to treat male pattern hair loss. Specifically, it works by lowering levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles in men who are genetically predisposed to baldness. As a result, reducing DHT helps slow ongoing hair loss and may promote regrowth in some men.
What Propecia Is
Propecia (generic name: Finasteride 1 mg) is an FDA-approved pill used to treat male pattern hair loss, also called androgenetic alopecia.
It works by lowering a hormone called DHT (dihydrotestosterone). This hormone causes hair follicles to shrink in men who are genetically prone to hair loss. As a result, lowering DHT helps protect those follicles.
How It Works
First, the body converts testosterone into DHT through an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase.
Next, DHT attaches to sensitive hair follicles and makes them shrink over time.
Then, finasteride blocks the Type II form of 5-alpha reductase.
Because of this, scalp DHT levels drop by about 60–70%.
As a result, hair loss usually slows down, and in some men, hair may regrow.
Who It’s Best For
Propecia works best for:
-
Men with early to moderate male pattern baldness
-
Men thinning at the crown (top of the head)
-
Men with early frontal thinning
However, it is not approved for women.
Most importantly, starting treatment early usually leads to better results.
Dosage & How to Take It
The standard dose is 1 mg once daily.
You should take it at the same time every day. You can take it with or without food.
Also, do not crush or split the tablet.
Above all, consistency matters. If you stop taking it, the benefits usually fade within 6–12 months.
Timeline of Results
-
1–3 months: You may notice some early shedding.
-
3–6 months: Hair loss usually stabilizes.
-
6–12 months: Visible improvement may appear.
-
12 months: This is the best time to evaluate full results.
Possible Side Effects (Uncommon)
Side effects are possible but uncommon. They may include:
-
Reduced sex drive
-
Erectile dysfunction
-
Lower semen volume
-
Breast tenderness (rare)
-
Mood changes (rare)
These effects were reported in about 1–3% of men in clinical trials. In most cases, they improve after stopping the medication.
Using It With Other Treatments
Many men combine finasteride with other treatments. For example:
-
Minoxidil (Rogaine)
-
Microneedling
-
Ketoconazole shampoo
This is helpful because combination therapy targets hair loss in different ways — both hormone-related and blood-flow related pathways.
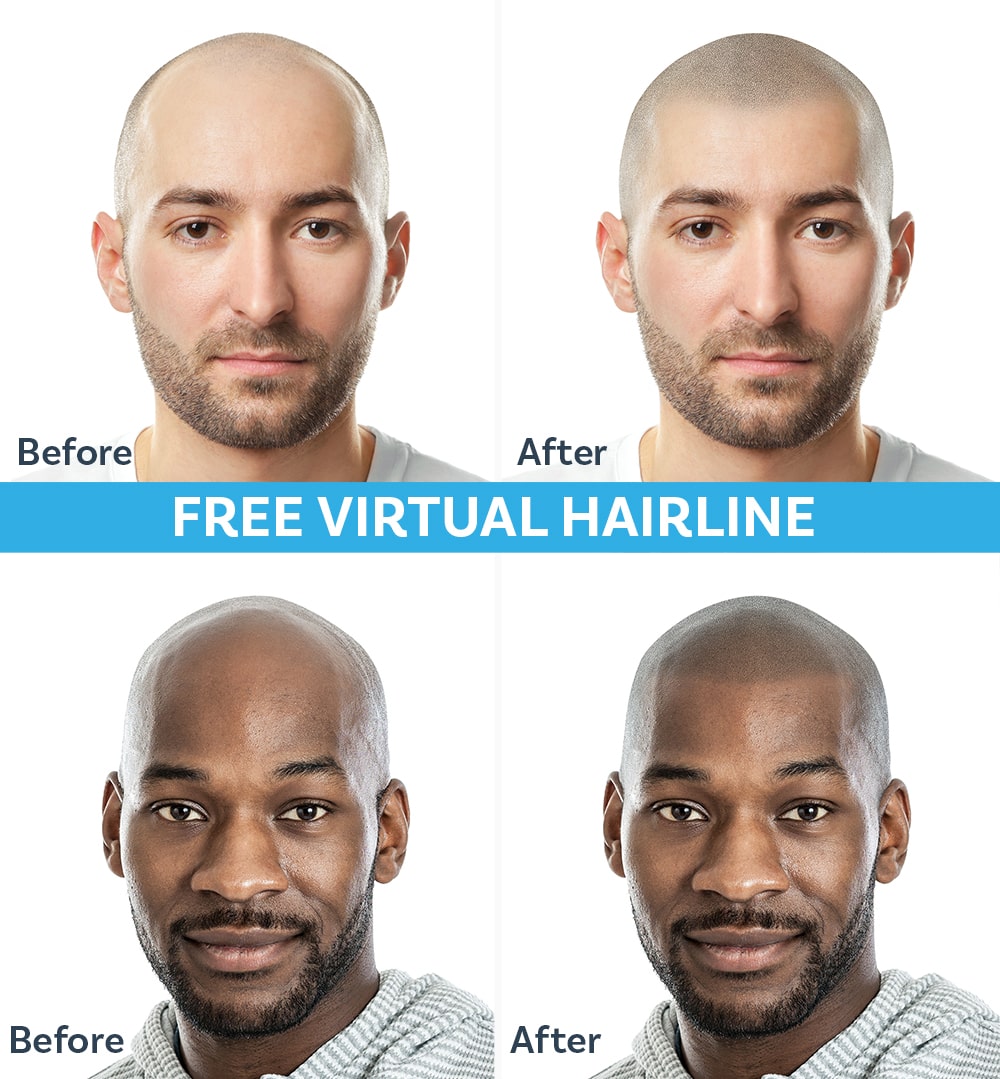
Alternative: Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP)
Scalp micropigmentation is a non-surgical cosmetic procedure that deposits pigment into the scalp to create the illusion of hair follicles.
It does not regrow hair — it creates the appearance of density.
How SMP Compares to Finasteride
| Factor | Finasteride | Scalp Micropigmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Stops hair loss | Yes (in most men) | No |
| Regrows hair | Sometimes | No |
| Requires daily use | Yes | No |
| Surgical | No | No (cosmetic tattoo) |
| Permanent effect | Only while taking | Semi-permanent (3–6 years before touch-up) |
| Side effects | Possible hormonal | Minimal (localized irritation) |
Who Might Choose SMP Instead?
SMP may be a better option for some men. For example, men who do not want to take hormonal medications often prefer it. In addition, those who experienced side effects from finasteride may look for a non-medical alternative.
Similarly, men with advanced baldness—where regrowth is unlikely—often find SMP more practical. Finally, individuals who prefer a clean, shaved-head aesthetic may choose SMP to enhance that look.
Strategic Decision Framework
First, choose Finasteride if:
-
You want to preserve existing hair.
-
You’re early in the hair-loss progression curve.
-
You’re comfortable committing to a daily oral medication.
In contrast, choose SMP (Scalp Micropigmentation) if:
-
You want immediate visual density.
-
You prefer to avoid systemic medication.
-
You’re looking for a cosmetic enhancement rather than a biological intervention.
Ultimately, many men adopt a hybrid strategy — using finasteride to stabilize ongoing follicular miniaturization while leveraging SMP to optimize perceived density and hairline definition.
Bottom Line
Finasteride is a biologically active treatment that slows progression and can stimulate regrowth.
Scalp micropigmentation is a cosmetic illusion solution that improves appearance without altering hair biology.
The optimal choice depends on your stage of hair loss, risk tolerance, and aesthetic goals.
We have clinics in London and Manchester.
Book an appointment for a complimentary consultation today
Top posts: